ACIBADEM MASLAK HOSPITAL
International Joint Center (IJC)
Acıbadem University International Joint Center provides services in the diagnosis and treatment of many joint disorders. The medical technology devices and modern treatment methods used in the center accelerate the healing processes of the patients and increase the success rates of the treatment.

International Team of
Experts in the Field
International Team of
Experts in the Field
One of the most frequently asked questions after prosthesis surgery is the lifespan of the prosthesis. Knee and hip prostheses generally have a lifespan of 25-35 years. However, this duration may vary depending on personal factors. The patient's age, body weight, physical activity level and post-surgical care are the main factors affecting the lifespan of the prosthesis.
In younger and more active patients, the lifespan of the prosthesis may be shorter, whereas in older and less active individuals, the prosthesis may last longer. Among the most common reasons for prosthesis replacement, wear and loosening are the most important reasons that shorten the lifespan of the prosthesis.
To prolong the lifespan of the prosthesis, it is important to follow the doctor's recommendations, have regular check-ups and avoid excessive physical activity. While the lifespan of prostheses can be extended with new generation materials and surgical techniques, it may be necessary to replace the prosthesis after a certain period of time.
In order for the prosthesis to function in a long-lasting and healthy way, it is important to keep the wound area clean in the early postoperative period and to pay attention to the doctor's recommendations against the risk of infection.
In daily life, heavy lifting and excessive physical activity should be avoided. In addition, weight control can prevent excessive pressure on the prosthesis and prolong its lifespan.
Immediate consultation with a doctor is crucial if there is any pain, swelling or restriction of movement in the prosthetic joint. Regular medical check-ups and X-rays are important for monitoring the condition of the prosthesis and detecting potential problems early.
Replacement surgeries are usually performed successfully and improve the quality of life of patients. However, like any surgical intervention, replacement surgeries also have some risks. Infection is one of the risks and may develop at the surgical site. To reduce the risk of infection, hygiene rules should be observed in the postoperative period.
Other risks include clots in the veins in the legs and blockage of a blood vessel in the lung (embolism). This can block blood circulation and lead to serious health problems. Blood thinners and leg exercises can help prevent clots from forming. There is also a risk of prosthesis loosening or dislodging, which is usually caused by prolonged use of the prosthesis or excessive physical activity. In rare cases, fractures can occur in the bones around the prosthesis. In order to reduce such risks, it is important to follow the doctor's recommendations before and after surgery and to keep regular check-ups. However, despite all these risks, replacement surgeries usually greatly improve the quality of life of patients.
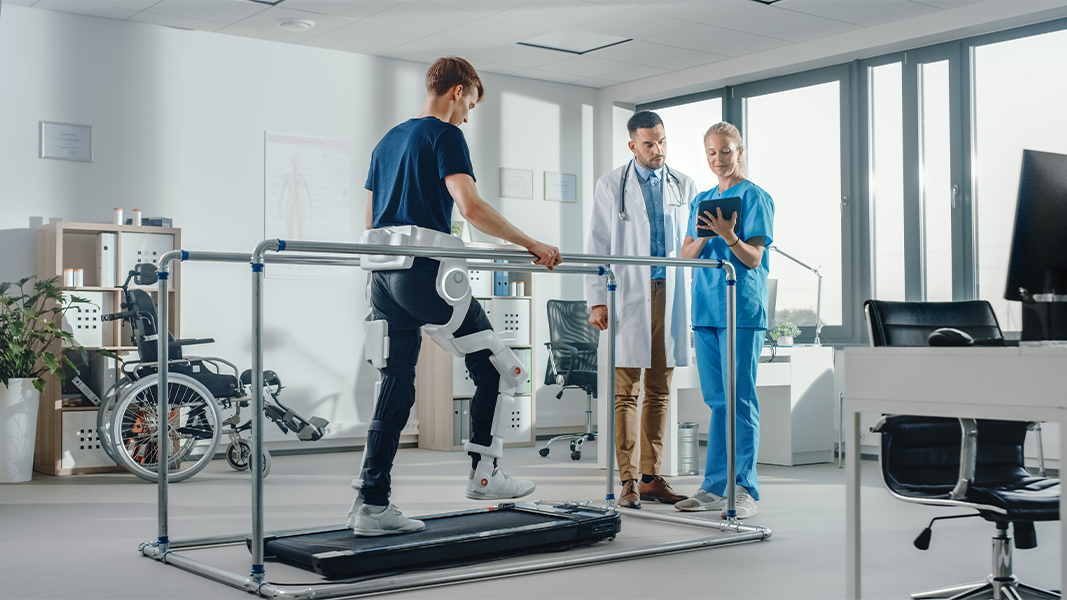
Rehabilitation plays a critical role for a successful recovery after replacement surgery. Post-operative rehabilitation is important for both knee and hip replacement surgeries to regain mobility and to be able to perform daily activities without any problems. The rehabilitation process is individualized according to the patient's condition and is typically carried out under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
In the initial stages, strengthening of the leg muscles with light exercises and walking is targeted. During this period, it is aimed to strengthen the muscles around the prosthetic joint, increase joint stability and improve blood circulation.
In addition, patients are also trained to improve their balance and walking style in the postoperative period. Attending regular rehabilitation sessions helps prevent possible complications and accelerates the healing process. Postoperative rehabilitation is an indispensable process for patients to regain their independence and improve their quality of life. Sticking to the recommendations of the doctor and physiotherapist ensures that the rehabilitation process is the most efficient.
What Causes Joint Pain?
Joint pain can be caused by many different conditions involving the joints. The most common ones include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, bursitis, tendonitis and joint injuries. Factors such as being overweight, inactivity and aging can also cause joint pain. It is therefore important to consult a specialist to determine the cause of joint pain and the appropriate treatment methods.
What is osteoarthritis and how is it treated?
Osteoarthritis is characterized by the wear of cartilage in joints over time and impaired joint function. Although this condition is usually associated with aging, overweight, joint injuries and genetic factors can also trigger osteoarthritis. Treatment includes painkillers, physical therapy, weight control and, in advanced cases, surgical interventions.
How to maintain joint health?
To maintain joint health, it is important to exercise regularly, maintain an ideal weight, eat a balanced diet and avoid overloading the joints. Also, using joint protectors, especially when practicing sports, avoiding sudden movements and engaging in exercises that strengthen the muscles also support joint health.
When is joint replacement necessary?
Joint replacement is necessary in cases such as severe damage to the joint or severe osteoarthritis, where other treatment methods are inadequate and severely affect daily life. Replacement surgery improves the mobility of the joint, reducing pain and improving the patient's quality of life. The surgeon assesses the patient's general health, age and lifestyle to determine whether they are suitable for prosthetic surgery.
How are joint injuries treated?
Joint injuries require different treatment methods depending on the severity of the injury. For mild injuries, rest, ice, compression and elevation are recommended, while more serious injuries may require physical therapy, medication and in some cases surgery. It is important to seek the help of a specialized orthopedist to determine a treatment plan based on the type of injury.
How to recognize joint inflammation (arthritis)?
Joint inflammation, with or without germs, is usually characterized by swelling, pain, stiffness and limitation of movement in the joint. In non-microbial joint inflammation, feeling stiff in the joints in the morning is a common symptom of arthritis. A medical examination and some blood tests may be needed to determine the type and severity of arthritis. Early diagnosis is critical in the treatment process to prevent joint damage.
How does exercise contribute to joint health?
Regular exercise strengthens the muscles around the joints, improving joint stability and maintaining joint health. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking and cycling increase mobility without straining the joints. Regular exercise also helps maintain joint mobility and reduces the risk of osteoarthritis.
Which natural remedies can be used to relieve joint pain?
Natural remedies used to relieve joint pain include hot and cold therapy, herbal supplements (e.g. turmeric, ginger), acupuncture, massage and stretching exercises. It may also be helpful to consume foods with omega-3 fatty acids and anti-inflammatory properties to relieve joint pain. However, it is important to consult a doctor before resorting to these remedies.
How long do knee and hip replacements last?
Knee and hip replacements usually have a lifespan between 25-35 years. However, this period may vary depending on the patient's age, physical activity level, body weight and the material properties of the prosthesis. To prolong the lifespan of the prosthesis, regular medical check-ups, avoiding excessive physical activity and adopting a healthy lifestyle are important.